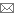
Trade Tricks: Selective FocusUsing depth of field creatively |

|
|
|
Primarily controlled in-camera, depth of field is a combination of three variables: lens aperture (ƒ-stop), lens focal length and your distance from the focal point. Of these three, the aperture has the most influence. To increase or deepen depth of field: 1) Select smaller apertures like ƒ/8, ƒ/11 and ƒ/16; and/or 2) Choose a short focal length on a wide-angle or a fish-eye lens; and/or 3) Move farther away from your primary subject. To decrease or narrow depth of field: 1) Select larger apertures like ƒ/2.8 and ƒ/4; and/or 2) Choose a longer focal length on a fast tele-zoom lens; and/or 3) Move closer to your primary subject. ExpoAperture2 Depth-Of-Field Guide If you want an accurate, simple way to determine what aperture to select to achieve a desired depth of field, the ExpoAperture2 Depth-of-Field Guide (www.expoimaging.net) is an excellent tool. In making calculations, set the first of two moveable dials to the camera format and the size of either the film or the image sensor. This is important because a focal length of 40mm at ƒ/8 on a 35mm SLR, for instance, won’t have the same depth of field on a D-SLR with a sensor that’s smaller than a 35mm piece of film.  Then turn the guide over and use the distance dial on the back to estimate how far it is (in inches or feet) to your focal point and the range of distance around that point you want to be in sharpest focus. The range of distance is represented by focus zones, 15 in all. So if you want everything from 7½ feet to infinity to be in sharp focus, for example, that translates to four focus zones. Then turn the guide over and use the distance dial on the back to estimate how far it is (in inches or feet) to your focal point and the range of distance around that point you want to be in sharpest focus. The range of distance is represented by focus zones, 15 in all. So if you want everything from 7½ feet to infinity to be in sharp focus, for example, that translates to four focus zones. Flip the guide back over, and with the sensor-size/format dial set correctly, turn the second dial so that the focal length you want (from 15mm to 135mm) appears in the little window. Then find the number four on the edge of the dial and the corresponding ƒ-stop listed above. Although many D-SLRs have a depth-of-field preview, the usefulness of the feature is somewhat limited compared to the accuracy of the ExpoAperture2. Previews for macro photography are decent when using large apertures and long focal lengths because they’re easy to see on the LCD. But when it comes to wide-angle landscape or cityscape shots, where you want to preview a small aperture and short focal length, there’s no way to tell on a 2½- or 3-inch screen how that depth of field will affect image detail and the range of sharpness around your focal point when reproduced on a large print. Learning to use depth of field creatively takes a little extra experimentation and forethought, but you’ll quickly see the dramatic effects that selective focus can have on your images. |



 Using selective focus is a powerful technique to help frame and present your subject. Playing with depth of field will help transform your image from one that looks like a quick snapshot to one that shows you’ve put some creative thought into how you want to present your subject.
Using selective focus is a powerful technique to help frame and present your subject. Playing with depth of field will help transform your image from one that looks like a quick snapshot to one that shows you’ve put some creative thought into how you want to present your subject. 



















